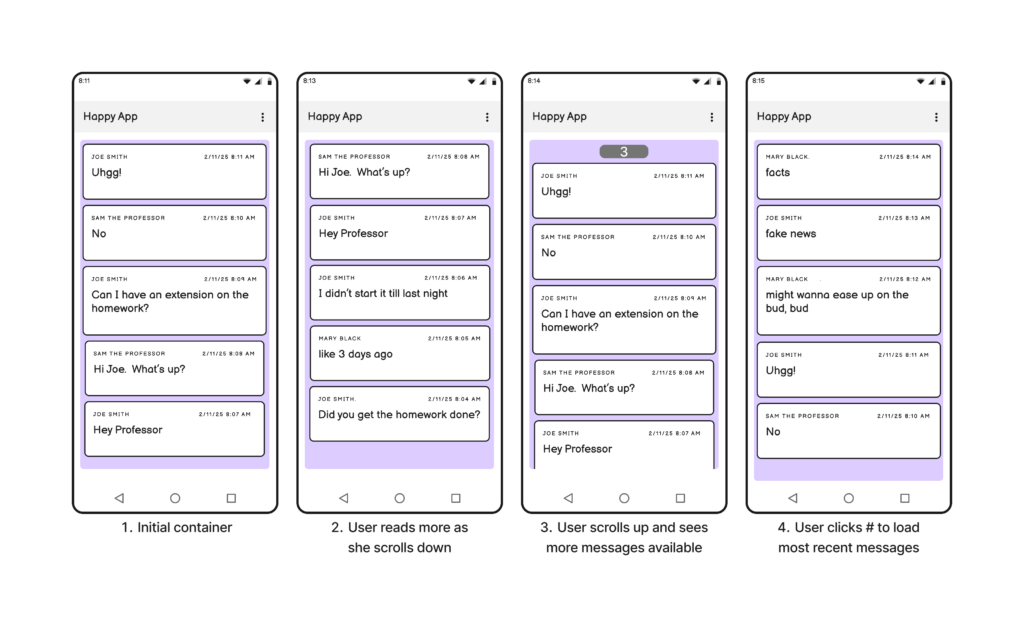
In this assignment you’ll add a scrollable container that allows the user to potentially read all of the messages in the database.
Create a Message Component
To accomplish this, first create a component that can displays a single message. The message’s data (sender’s name, date/time, and message text) should come into the component via props defined by the component. The API server will send your app an array of message objects with each object using the following properties:
- senderName
- updatedAt
- text
It therefore makes sense to give your props the same names.
Create a Scrollable Container Component
Next, create a scrollable message container component that you can place in any view. The component should behave as depicted in the image shown above.
- When initially started, the app will fetch enough messages to slightly overflow the container.
- When the user scrolls down to the bottom of the list of messages, the app will fetch additional older messages for the user to read.
- When the user scrolls back up to the top, the app will display the number of new messages (if any) that can be fetched.
- If the user clicks on the number, the app downloads the new messages and adds them to the top of the list.
You may want to use an IntersectionObserver (like we did in CSCI-230) to detect when the user has reached the bottom of the list of messages so that more can be fetched.
The API
The API server has 2 new endpoints to help serve up messages to your app. One endpoint returns a set of messages, and the other returns an integer indicating how many new messages are available. Below are specifications for the endpoints.
Note that all DateTime strings for these endpoints are transmitted as ISO 8601 strings which can be created using Date.toISOString(). Dates are in UTC time which is 5 hours ahead of EST. For example, 6:00 am on May 12, 2023 can be written with EST time and an offset (2023-05-12T06:00:00.000-05:00) or directly in UTC time with ‘Z’ at the end (2023-05-12T11:00:00.000Z) or as you can see in the MongoDB database in UTC time with a 0 offset (2023-05-12T11:00:00.000+00:00).
Both endpoints use query strings to pass data to the API server rather than passing data via the body. A query string is a part of a URL and is appended after the endpoint. A query string starts with a question mark (?) which is followed by one or more key=value strings. The key=value strings are separated by ampersands (&).
For example the URL to get at most 5 messages whose updateAt timestamp is before approximately 6:00 am UTC on 2/11/25 would be:
https://hap-app-api.azurewebsites.net/messages?limit=5&before=2025-02-11T06:00:00.321Z
Getting Messages
The GET /messages endpoint returns an array of messages.
Below are descriptions for each query string.
after=DateTime(only return messages whose updatedAt timestamps are after the DateTime specified)before=DateTime(only return messages whose updatedAt timestamps are before the DateTime specified)limit=N(return at most N messages)
Getting the Number of New Messages Available to Download
The GET /messages/count endpoint returns the total number of messages that have been posted in the database since the DateTime specified.
after=DateTime(count only the messages whose updatedAt timestamps are after the DateTime specified)